Around one in five adults worldwide now lives with obesity, and international targets have fallen behind reality.
Health systems already carry the cost. High BMI adds close to $1 trillion each year to global healthcare spending, about 13% of the total. Higher rates of diabetes, heart disease, and some cancers mean longer treatment, heavier use of medicine, and growing pressure on public budgets.
Governments are committed to global health goals, yet progress failed to match the scale of the problem.
Public health experts now call for direct action: earlier support for people at risk, wider access to effective treatment, and prevention policies that make healthier food and daily movement easier choices for the population as a whole.
Key Takeaways
- 1 in 5 adults have obesity by 2025, with low-income countries seeing the fastest rise.
- Obesity raises risks for diabetes, heart disease, and cancer, affecting millions.
- $990 billion is spent yearly on obesity-related healthcare, 17.7% in the Americas.
- Pacific Islands have the highest obesity rates, exceeding 50% in some nations.
- Obesity is not just a personal choice; genetic, economic, and environmental factors play a role.
- Urgent action needed: Governments must invest in prevention, treatment, and policy change.
Uniting for a Stronger Response to Obesity
On March 4, 2020, obesity organizations worldwide are joining forces to mark World Obesity Day, advocating for comprehensive solutions, improved treatment, and shared accountability in addressing the global obesity epidemic.
Obesity is a chronic, relapsing disease that continues to affect a rapidly growing number of people across the globe. A new report by the World Obesity Federation, released today, underscores the alarming rise in obesity rates and warns that all countries are falling short of the 2025 global targets, despite just five years remaining.
Projected Global Obesity Trends
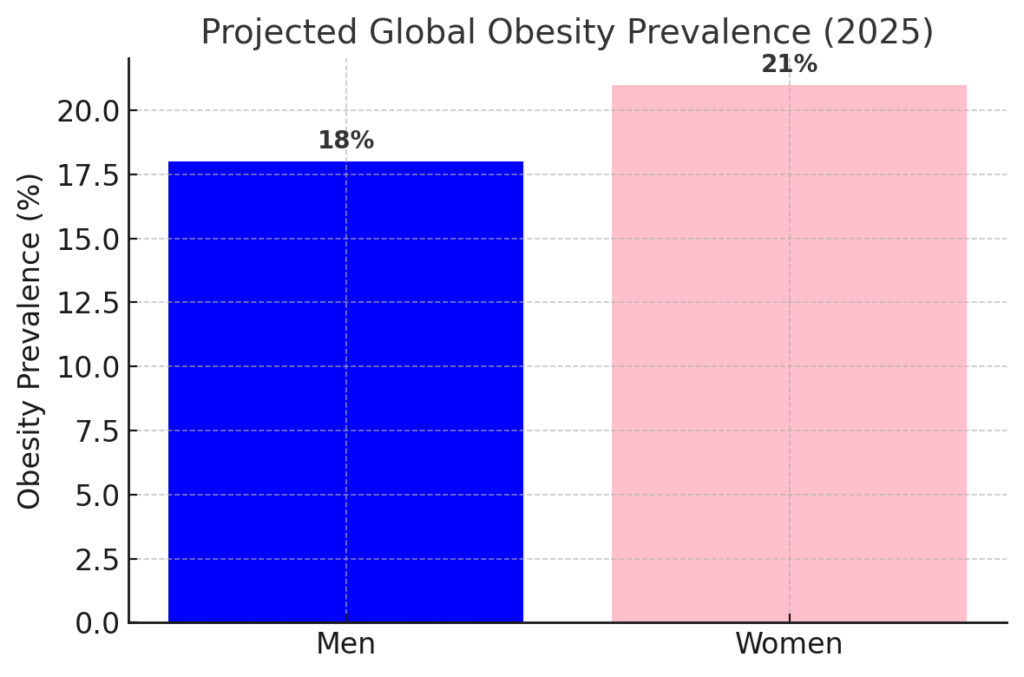
By 2025, global obesity prevalence is expected to reach 18% in men and exceed 21% in women, according to NIH.
Certain countries are experiencing far higher obesity levels, with five nations, the United States, China, Brazil, India, and Russia, accounting for nearly one-third of all adult obesity cases worldwide.
Projected Global Obesity Prevalence (2025)
Global Obesity Prevalence in Adults (2016)
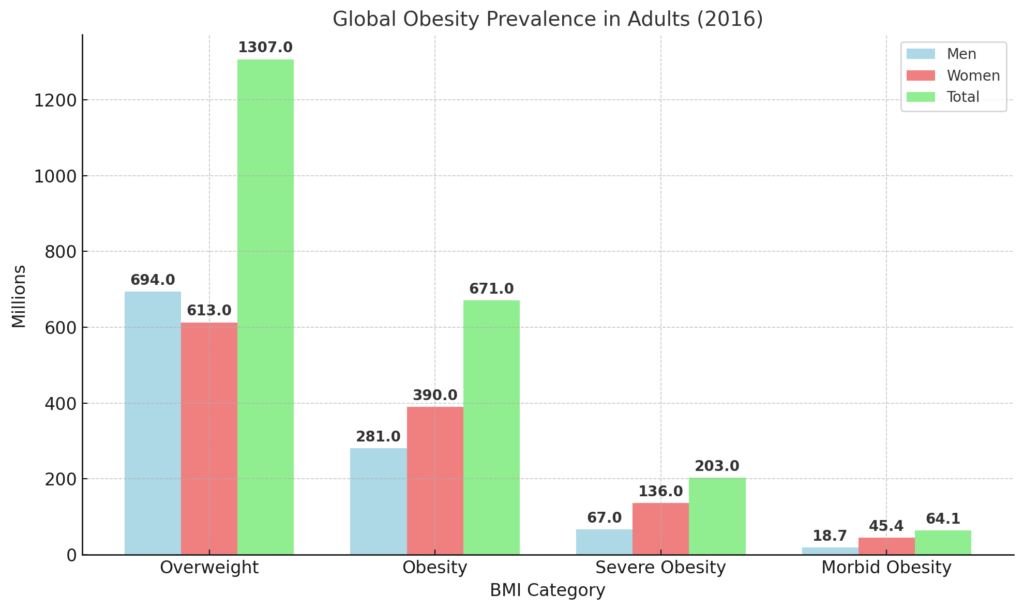
Over 1.3 billion adults were overweight in 2016, highlighting a widespread issue.
671 million adults were classified as obese, indicating that obesity is a growing public health crisis according to the WHO.
The number of women with obesity and severe obesity is significantly higher than men, pointing to gender-based health disparities.
A Growing Crisis in Developing Nations
Once considered a problem primarily in high-income countries, obesity is now rising fastest in low- and middle-income nations. Countries such as Vietnam, Indonesia, and Bangladesh are witnessing some of the most rapid increases in obesity rates.
Many of these nations continue to struggle with undernutrition, creating a double burden of malnutrition. Meanwhile, regions like the Pacific Islands and the Middle East report exceptionally high obesity prevalence, with rates reaching up to two-thirds of adults in some countries.
Countries Experiencing the Fastest Obesity Growth (CAGR % per year, 1995-2016)
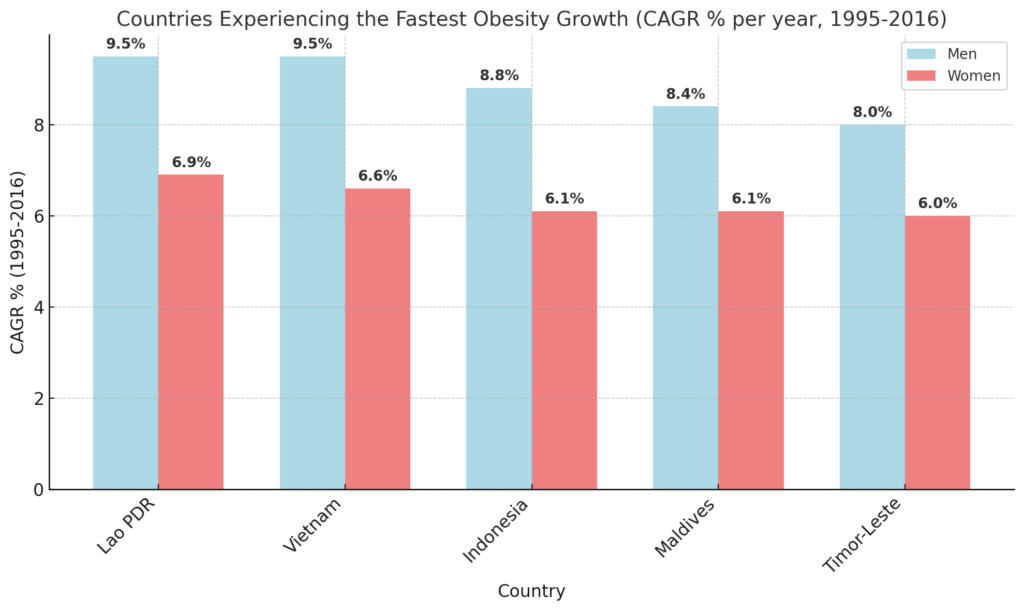
A study from NCBI notes that Southeast Asian countries, particularly Vietnam, Indonesia, and Lao PDR, are witnessing the most rapid rise in obesity.
The trend suggests urbanization, economic changes, and dietary shifts are accelerating obesity rates in low- and middle-income countries.
The rise in obesity in low-income countries adds strain to health systems already struggling with undernutrition, creating a double burden of malnutrition.
Countries with the Highest Prevalence of Obesity
Some nations are already experiencing alarmingly high obesity rates, particularly in the Pacific Islands.
Countries with the Highest Obesity Prevalence (% of adults with BMI ≥30)
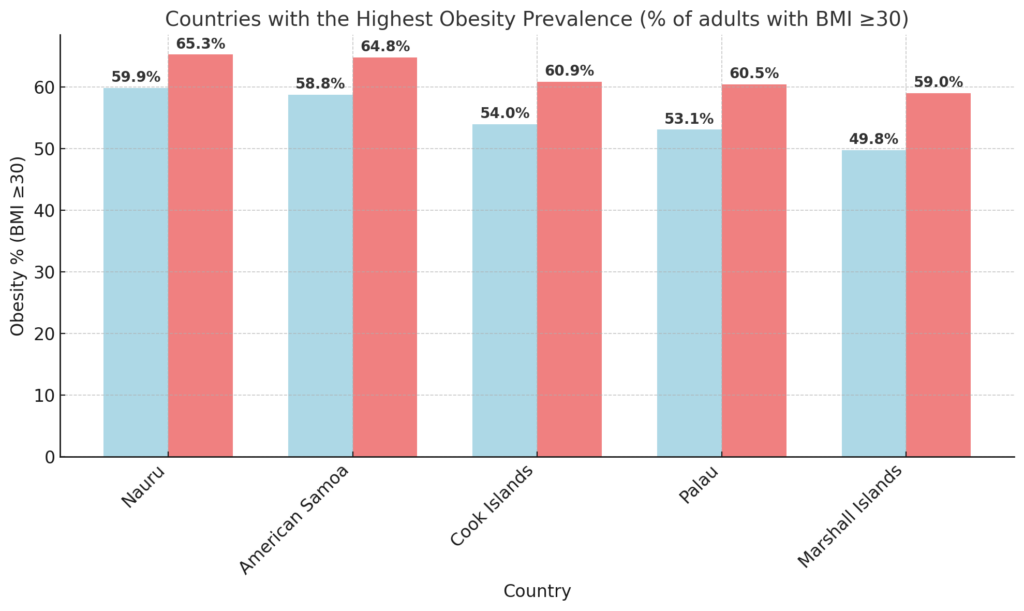
Pacific Island nations dominate the list, with over 50% of their populations classified as obese.
The high prevalence is linked to a shift from traditional diets to high-calorie, processed foods, coupled with reduced physical activity.
These countries face an increased burden of obesity-related diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and hypertension.
Health Impacts of Untreated Obesity
The WHO also notes that if obesity is left unaddressed, it will continue to escalate, increasing the risk of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer.
These conditions threaten progress on other WHO NCD targets.
A high BMI has already been linked to:
- 217.6 million cases of diabetes
- 307 million cases of hypertension
- 11.7 million cases of cardiovascular disease
- Nearly 500,000 cases of certain cancers
The Financial and Social Burden of Obesity
We need to lighten the economic burden of #obesity. On #WorldObesityDay, find out what governments can do: 👉 https://t.co/K9CZ13Y8q6 #overweight #ChildhoodObesity pic.twitter.com/V8TU7OJzM4
— OECD Social (@OECD_Social) October 11, 2019
Beyond its impact on health, obesity places an enormous economic strain on healthcare systems and affects employment, education, and mental well-being. The stigma and misconceptions surrounding obesity further exacerbate its social consequences.
Estimated Cost of High BMI on Healthcare Systems
In OECD countries, obesity is projected to cost 3.3% of total GDP, with the highest economic impact observed in Mexico (5.3%) and Brazil (5%).
| WHO Region | Total Healthcare Expenditure (US$ bn) | Attributable to High BMI (US$ bn) | % of Total Healthcare Spending |
| Global | 7,482.3 | 990.6 | 13.2% |
| Region of the Americas | 3,784.3 | 669.2 | 17.7% |
| European Region | 1,921.4 | 218.5 | 11.4% |
| Eastern Mediterranean | 147.8 | 20.1 | 13.6% |
| African Region | 84.8 | 7.4 | 8.8% |
| South-East Asia | 141.9 | 4.8 | 3.4% |
Obesity-related healthcare costs total nearly $1 trillion annually, making up 13.2% of total global healthcare spending.
The highest regional healthcare costs due to obesity are in the Americas (17.7%), highlighting the severe economic impact in North and South America, as stated by NCBI.
In contrast, South-East Asia has the lowest attributable costs (3.4%), but this may increase as obesity rates rise in developing nations.
Breaking the Cycle of Stigma and Misconceptions
View this post on Instagram
Despite growing awareness, many people(including healthcare professionals and policymakers) continue to view obesity as a matter of personal responsibility rather than a complex, chronic disease.
In reality, obesity is influenced by genetic, psychological, sociocultural, economic, and environmental factors.
Today, organizations worldwide are calling for an end to the blame and shame culture, urging a re-evaluation of how obesity is understood and addressed.
Urgent Policy Action: A Global Declaration on Obesity
Professor Donna Ryan, President of the World Obesity Federation, emphasized the need for immediate action:
“Despite government commitments, no country is on track to meet WHO goals. There is no excuse for inaction. People with obesity deserve equitable access to treatment and prevention opportunities. Policymakers must take action to address the root causes of obesity.”
To mark the first unified World Obesity Day, a Global Declaration on Obesity has been launched, outlining five critical action areas, the ROOTS, that policymakers must address to meet their commitments.
Countries with the Best Chance of Meeting 2025 Obesity Targets
Some countries have made significant progress in obesity control and are most likely to meet the WHO targets.
Countries with the Best Chance of Meeting WHO 2025 Obesity Targets
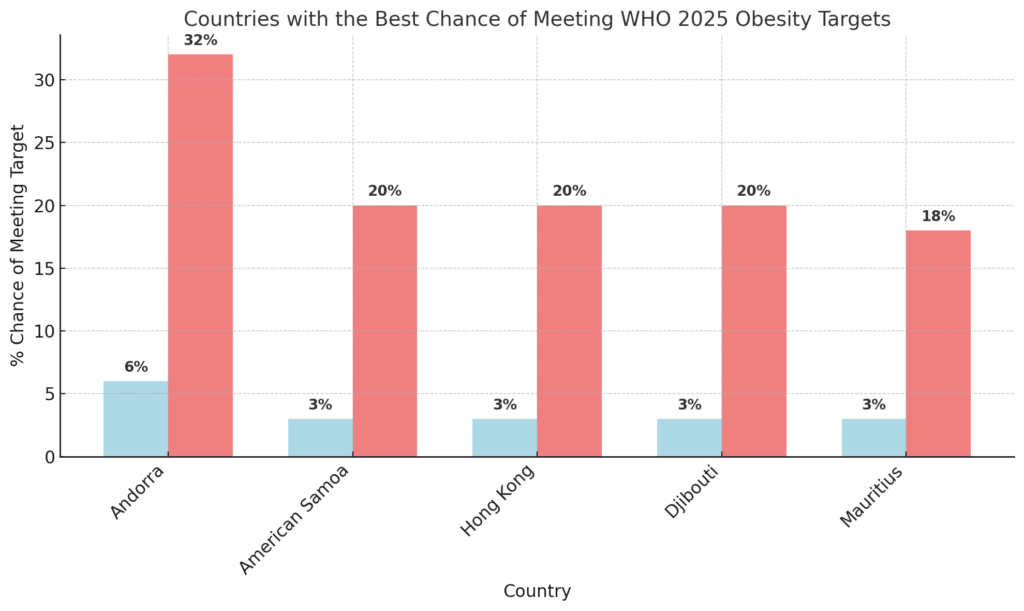
Andorra shows the best progress, with a 32% chance of meeting obesity targets for women and 6% for men.
Some unexpected nations, such as American Samoa and Djibouti, have also demonstrated some progress in addressing obesity.
More developed countries in Europe and Asia, such as Estonia, Latvia, and Hong Kong, show higher chances of meeting their targets than many high-obesity regions.
Bottom Line
Obesity has turned into a global problem that health systems and budgets keep absorbing year after year.
Rates keep rising fastest in low and middle-income countries, where clinics and public health programs already run under pressure.
High BMI drives more diabetes, heart disease, and some cancers, which means more long-term treatment and higher spending. Global targets for 2025 are slipping, so the window for cheaper, easier action keeps closing.
Governments need to put money into prevention, earlier support, and access to proven treatment, plus policies that make healthy food and active living easier choices for everyone.


